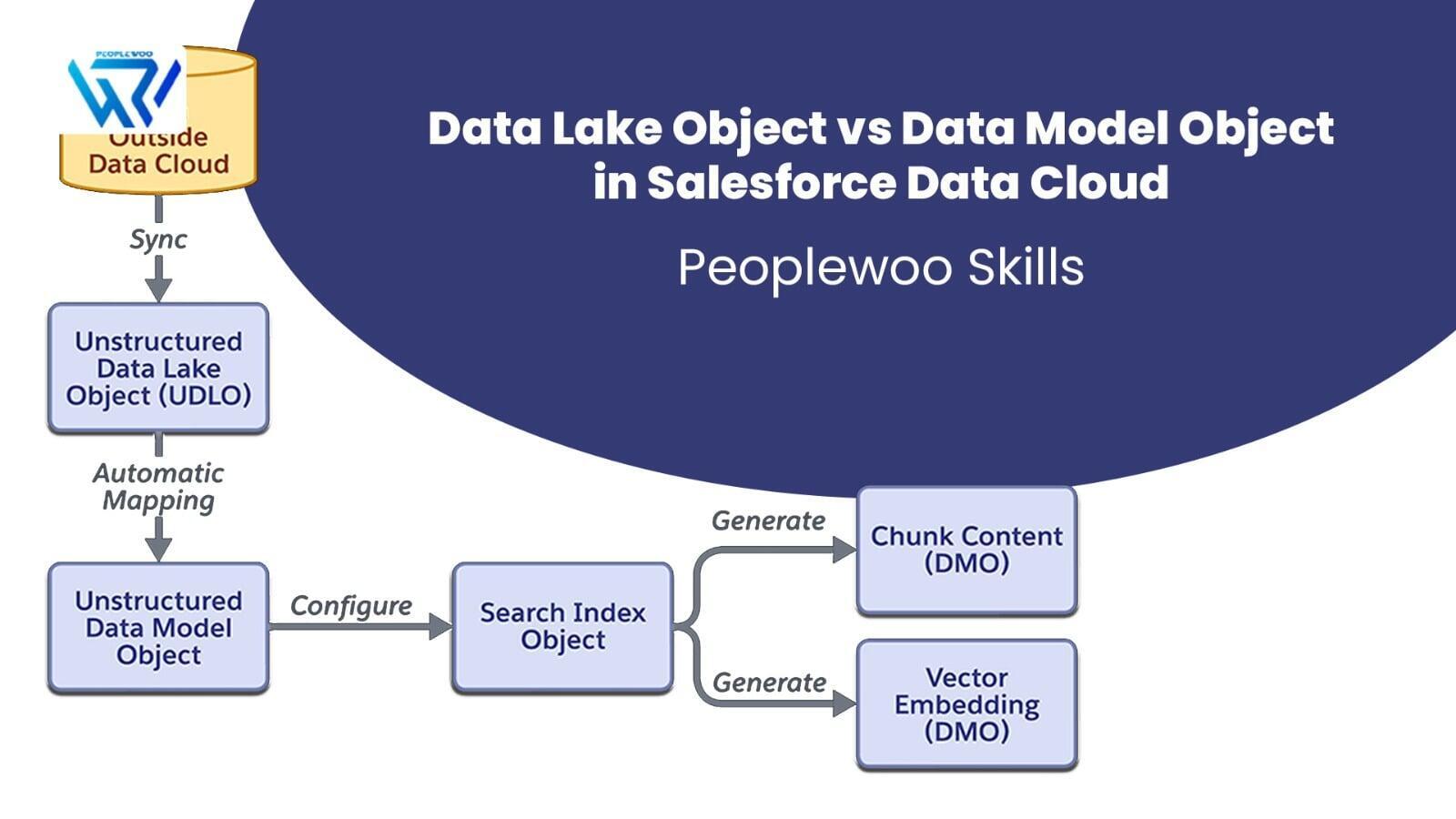
Salesforce Data Cloud uses two foundational object types to manage data: Data Lake Objects (DLOs) and Data Model Objects (DMOs). Understanding the difference between them is essential for building a unified, actionable customer profile.
In this article, you’ll learn the purpose, structure, and real-world usage of both object types—and when to use each—within Salesforce Data Cloud.
What is a Data Lake Object (DLO)?
A Data Lake Object is a raw storage object that holds the ingested data exactly as it was received from the source. Think of it as the staging layer in the architecture. Data Lake Objects help preserve original fields, formats, and structure for future reference, validation, or transformations.
- Stores unharmonized/raw data
- Used for auditing and re-mapping
- Not directly used for segmentation or identity resolution
What is a Data Model Object (DMO)?
A Data Model Object is a standardized object structure used by Salesforce to harmonize, unify, and activate customer data. DMOs map similar data (like email addresses, mobile numbers, purchase events) from different systems into a common format. This enables powerful identity resolution and segmentation.
- Stores harmonized and processed data
- Mapped via Data Streams
- Used in Unified Profile, Segments, and Calculated Insights
Watch Our Full Tutorial Video
Key Differences: DLO vs DMO
| Feature | Data Lake Object (DLO) | Data Model Object (DMO) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Raw data storage | Harmonized, unified data for activation |
| Editable | No (read-only) | Yes (via mappings) |
| Used in Segmentation | No | Yes |
| Supports Identity Resolution | No | Yes |
| Examples | Raw files from CRM or web click logs | Individual, Contact Point Email, Purchase Event |

How DLO and DMO Work Together
Data typically flows from source systems into Data Lake Objects (DLOs) via Data Streams. Then, through mapping and transformation, the data flows into the appropriate Data Model Objects (DMOs). This ensures data is preserved in its raw state while also being prepared for segmentation, personalization, and analytics.
Real-Life Example
Imagine a retail company that uploads purchase data from its ecommerce platform into a DLO. This raw data is then mapped to a DMO called Engagement Event, where it’s structured and linked to individual customers. The marketing team can then create segments such as “High-Value Repeat Buyers” for targeted campaigns.
Learn Data Cloud Hands-On
Struggling to map DLOs to DMOs or implement identity stitching? Join our expert-led Data Cloud training and master every layer of Salesforce's customer data platform with real-world demos.
Register Now
Best Practices
- Always validate your DLO before mapping to DMO
- Use standard DMOs unless absolutely necessary to create a custom one
- Keep naming conventions consistent for easier debugging
- Document every mapping for auditing and governance
Why Learn Data Cloud with Peoplewoo Skills?
- Live, instructor-led training with real-time practice
- Hands-on experience with Salesforce Data Cloud projects
- Access to sandbox orgs and datasets
- Free demo and career support
- Preparation for Salesforce certification
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Conclusion
Both Data Lake Objects (DLOs) and Data Model Objects (DMOs) are essential to Salesforce Data Cloud’s data unification process. While DLOs preserve raw, unprocessed data, DMOs provide the harmonized, ready-to-use version for segmentation, analytics, and activation. Mastering how these two layers interact is key to delivering precise customer insights and powerful marketing outcomes.
Take your Salesforce Data Cloud expertise to the next level.
More SFDC Resources
Start your SFMC journey today — join our Live Training or learn at your own pace with our Udemy Course.
Need help? Chat with us on WhatsApp anytime.
Learn. Practice. Get Certified. Succeed with Peoplewoo Skills.

